[This story was written by Giuseppe Ragonese, PT, DPT, CLT-LANA, a physical therapist with St. Peter’s Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation.]
March is Lymphedema Awareness Month, a time to increase awareness of this chronic and progressive disorder. Lymphedema results from an impaired lymphatic system, which helps the body regulate fluid levels and defend against infections.
Water, proteins, and other substances are always leaking out of tiny blood capillaries throughout the body and into the tissues around them. When the lymphatic system, which is part of the immune system, is compromised the lymph vessels are unable to adequately drain lymph fluid, usually from an arm or leg.
Lymphedema can either be primary or secondary. Primary lymphedema occurs from abnormal lymphatic formation, with swelling starting at birth or even into the teen years. Secondary lymphedema can have a number of causes including malignancy, obesity, trauma, surgery, and infection.
In the U.S., the most common cause of lymphedema is breast cancer. However, with the obesity pandemic growing, there is a subgroup of lymphedema patients that do not meet any lymphatic compromise other than being obese.
Signs and symptoms vary from person to person. However, common symptoms include the feeling of heaviness or tightness, limited range of motion of joints, recurring infections, and secondary skin changes.
Initially, swelling tends to be soft and “pitting” is often seen with an influx in fluid. With prolonged swelling, it is common for the skin to harden and thicken which is known as fibrosis. Changes in skin color may happen as well, known as hemosiderin staining, with the skin becoming stained a reddish-brown color from blood leaking out of the capillaries into the interstitium (the area just below the skin).
Since there is no cure for lymphedema, conservative treatment is most often used to manage the disease. Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) is the gold standard for lymphedema treatment. CDT traditionally has four parts:
Manual Lymph Drainage
A manual technique used to improve activity of lymph vessels, mobilize lymph fluid, and re-route lymph around blocked areas.
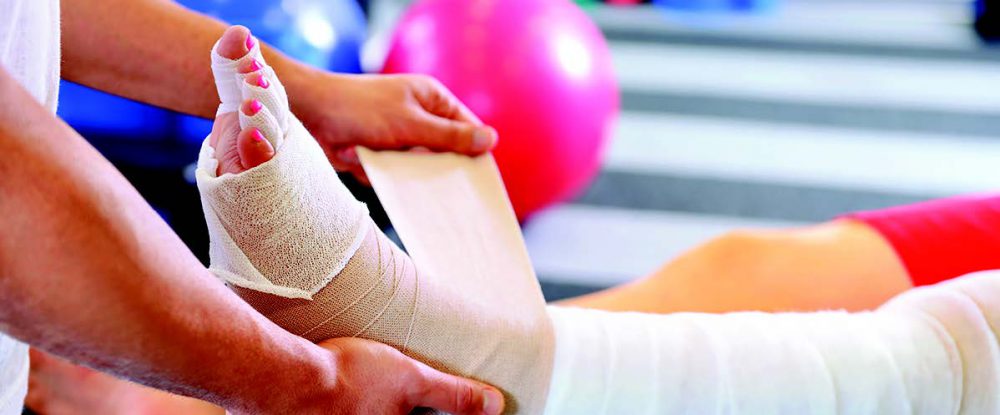
Compression Bandaging
A multi-layer bandaging system, used to create a gradient to push fluid out of the affected extremity.
Exercises
These assist with fluid return, as an internal pumping mechanism is created with movement, while strengthening musculature.
Skin Care
This is imperative, as good skin care reduces the risk of bacterial and fungal growth.
These four components encompass an acute “intensive” phase which is used to maximize the reduction of swelling in order to get the patient into an appropriate compression garment.
Though the four parts are pivotal, an education component is just as equally important. In some cases, patients come into the clinic to be seen by a certified lymphedema therapist without ever having heard the word lymphedema. So, most of the first session is spent educating a patient or family on the disease, its process, and what can be done to help them.
Once a patient is finally in their compression garment, there is a transition to the maintenance “self-management” phase. The goal here is for the patient to maintain the reduction in swelling from phase one. This is accomplished through the use of a daytime compression garment; a nighttime garment, if necessary; exercises; self-manual lymph drainage; and good skin hygiene.
St. Peter’s Health Partners offers multiple locations with certified lymphedema therapists who are available to educate and assist you with managing lymphedema. For more information, visit us at www.sphp.com/PT and search “lymphedema.”





